Let’s face it—accurate financial forecasting and planning isn’t everyone’s cup of tea, nor is it something someone would enjoy scratching their heads over.
In fact, it is considered to be the most difficult part of the business plan.
While it’s the most challenging aspect of business planning, it’s also the most important when convincing potential investors to invest in your business.
(You can’t simply ignore that!)
That’s why we decided to help you eat this giant frog at once. This is the ultimate guide to preparing a small business financial plan.
It will help you understand the critical components of financial planning, articulate quick steps to prepare a financial plan and provide a small business financial plan example to help you get started.
Sounds good? Let’s dive right in.
What is a Business Financial Plan?
A financial plan is an integral part of a business plan that helps determine if your business idea is sustainable and keeps you on track to financial health.
It’s the process of planning the financial aspects of a small business, which comprises its three major components: balance sheet, income statement, and cash-flow statement.
Besides these financial statements, this section may also include details about assets & liabilities, revenue and sales forecasts, break-even analysis, and others.
Key Takeaways
- Cash flow projection, balance sheet, and income statement are considered to be the three core components of a financial plan.
- Make sure to be realistic and conservative about your revenue forecasts; it is better to be surprised than disappointed.
- Preparing a financial plan is easier and faster when you use a financial planning tool.
- A clear market understanding, realistic assumptions, and thorough research are crucial to preparing reliable financial projections.
Why is Financial Planning Important to a Small Business?
It’s no secret and won’t come off as a big surprise that financial planning is crucial to building a successful business.
In fact, Y Combinator, a leading US startup accelerator, considered recent financial statements and projections to be critical elements of their Series A due diligence checklist.
A solid financial plan helps you manage cash flow, provides clear economic direction, helps you set realistic financial projections, and accounts for months when revenue might be lower than expected.
It helps you budget expenses, plan for yearly taxes, and show if your business is committed to its financial goals. It helps your investors understand where your business stands today and in 5 years.
Now that you know how important financial planning is for your small business, let’s head straight to discussing the critical elements of a financial plan.
Key Components of a Small Business Financial Plan
As mentioned earlier, cash flow projections, income statements, and balance sheets are three major components of a financial plan—but that’s not all. Here are all the key components you must consider including in your very own financial plan.
1. Income Statement
An income or profit and loss statement is a financial statement that shows any business’s income and expenditure over a specific time.
Your income statement also helps determine whether your business is making any profit or loss over a specific period—usually prepared at the end of the month, quarter, or year.
Your income or P&L statement must list the following:
- Cost of goods or cost of sale
- Operating expenses
- Revenue streams
- Gross margin
- EBITDA (Earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, & amortization)
2. Cash flow Statement
A cash flow statement is yet another important financial statement that summarizes the amount of cash and cash equivalents entering and leaving a business over a given time.
Your cash flow statement will consist of the following three components:
- Cash revenue projection
- Cash disbursement
- Cash flow reconciliation
Your company’s cash flow forecast can be critical while assessing your firm’s liquidity and ability to generate positive cash flows, pay off debts, and invest in growth initiatives.
3. Balance Sheet
A balance sheet is a financial statement that reports any company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity at a specific point in time. Your balance sheet is one of three major financial statements used in evaluating your company’s performance.
This statement consists of three parts: assets, liabilities, and the balance calculated by the difference between the first two. The final numbers on this sheet reflect the business owner’s equity or value.
Balance sheets follow the following accounting equation with liabilities plus owner equity on one side and assets on the other.
Here is what the core purpose of having a balance sheet:
- Indicates the capital need of the business
- It helps to identify the allocation of resources
- It calculates the requirement of seed money you put up, and
- How much financing is required?
Considering it’s a critical element in helping investors understand the current condition of your business, this is something you can’t simply miss out on.
4. Break-even Analysis
A break-even analysis is referred to as a financial calculation that weighs the costs of a new business, product, or service against the unit sell price to determine a point at which you have sold enough units to cover all your costs.
Your break-even point helps you understand when your investment is returned dollar-to-dollar, no more or less. This is the point where your small business is neither making profits nor burning cash.
However, anything you sell beyond that will result in profits.
Break-even analysis can be mandatory in situations when you either plan to expand your business, lower your pricing, or narrow down your business scenarios.
5. Sales forecast
Your sales forecast is a process of estimating your expected future revenue. It estimates how much your business plans to sell within the next month, quarter, year, or so. Your sales projection needs to be consistent with the sales number within your profit and loss statement.
Segmentation of these forecasts will depend on how closely you want to monitor your sales revenue. For instance, if you are a restaurant business, you may consider keeping catering and dine-in revenues separate from each other.
6. Expense Budget
Managing expenses is one of the fundamentals of your financial plan, and it starts with an expense budget. The expense budgets can include operating expenses, direct costs, or repaying debts.
Consider it as an informed prediction of your future business expenses based on your research, experience, and common sense.
Having covered all the key elements of a solid financial plan, let’s discuss creating one.
How to Create a Financial Section of a Business Plan?
1. Create a Strategic Plan
A strategic plan helps you understand what you want to accomplish with your financial plan. You may consider your operational expenses, financing needs, objectives, and exit strategy while creating a strategic plan.
You can start by asking yourself a few questions, like how much financing you need, where most of your expenses go, and what other resources will you need.
Once you determine your financial needs, set realistic goals based on these requirements—identifying your business KPIs would make an excellent starting point.
2. Choose the Right Financial Planning Tool
It may take you forever to start and finish creating a financial plan using traditional and old-school methods.
It worked just fine earlier, but that’s not how you do it today.
Having a financial forecasting tool will not just simplify the process, but will also help speed things up. In fact, it’s the best way to prepare financial forecasts and meet financial obligations.

Pro-tip
Create a Financial Plan with Upmetrics in no time
Enter your Financial Assumptions, and we’ll calculate your monthly/quarterly and yearly financial projections.

3. Make Presumptions to Project Financials
Of course, Upmetrics will help with automatic and accurate forecasting, but at least you have to feed it some information to get started. Right?
That’s why the next step—making predictions about your business financials.
It’s just about predicting your business growth and financial future based on its current performance and past financial records, so no need to overthink or complicate things.
Start off by gathering historical financial data, conducting industry research, and compiling relevant documents about your business and industry.
Once you have developed rough assumptions and understand your business finances, you can start preparing financial projections.
4. Prepare Realistic Financial Projections
Here we come—discussing the most important steps of all. Although it’s challenging to get through, Upmetrics’ forecasting tool makes it relatively easier for rookie entrepreneurs to follow.
Upmetrics allows you to forecast financials for up to 7 years, while new startups usually consider planning only for the next five years.
However, this is something that varies from business to business based on their financial goals and investor specifications, so it’s up to you how you plan your projections.
Following are the two key aspects of your financial projections:
Revenue Projections
Since your revenue projections help investors understand how much revenue your business plans to generate in the near future, it’s an important one for them to consider.
It generally involves conducting market research, determining pricing strategy, and cash flow forecast—which we’ve already discussed in the previous steps.
The following would be the key components of your revenue projections:
- Market analysis
- Sales forecast
- Pricing strategy
- Revenue streams
- Growth assumptions
- Seasonal variations
Expense Projections
Although both are different, revenue and expense forecasts are closely related to each other.
Similar to how revenue forecasts project revenue predictions, expense projections will predict expenses or future costs associated with operating a small business.
The following would be the key components of your expense projections:
- Fixed costs
- Variable costs
- Employee costs or payroll expenses
- Operational costs
- Marketing and advertising expenses
- Emergency fund
Remember, a clear understanding of your industry and market, realistic presumptions, and thorough research are the key to reliable financial projections.
5. “What if” Scenarios and Sensitivity Analysis
We learned to forecast financials, next—let’s discuss conducting sensitivity analysis to understand potential risks and opportunities involved in your business operations.
“What if” scenario or sensitivity analysis analyzes a business in three scenarios: best, expected, and worst-case. It increases transparency and helps investors and lenders understand your business’s future considering all three scenarios.
This proactive exercise will help make necessary adjustments to your financial plan and will be of incredible use in making strategic decisions.
6. Track Progress and Adjust Your Financial Plan
This may not sound like a necessary step while creating a financial plan, but it’s also an important one.
It’s critical to closely monitor your assumptions and make adjustments to make sure the assumptions you made are still relevant and you are heading in the right direction.
There won’t be any complex data analysis or big calculations, so worry not!
You simply have to compare your assumptions with the actual numbers to stay relevant. You may consider key business metrics to do so, like the number of customers acquired, cost per acquisition, or any other specific metrics.
Consider making adjustments if your assumptions do not resonate or match actual numbers.
And it was the last step in our financial plan writing guide. Next? Here’s a business financial plan example to help you get started.
Small Business Financial Plan Example
Since we’ve already learned about small business financial planning, let’s quickly review the coffee shop financial plan example created using Upmetrics:
Important Assumptions
- The sales forecast is conservative and assumes a 5% increase in Year 2 and a 10% in Year 3.
- The analysis accounts for economic seasonality – wherein some month’s revenues peak (such as holidays ) and wane in slower months.
- The analysis assumes the owner will not withdraw any salary till the 3rd year; at any time, it is assumed that the owner’s withdrawal is available at his discretion.
- Sales are on a cash basis – nonaccrual accounting.
- Moderate ramp-up in staff over the 5 years forecast
- Barista’s salary in the forecast is $36,000 in 2023.
- In general, most cafes have an 85% gross profit margin.
- In general, most cafes have a 3% net profit margin.
Projected Balance Sheet
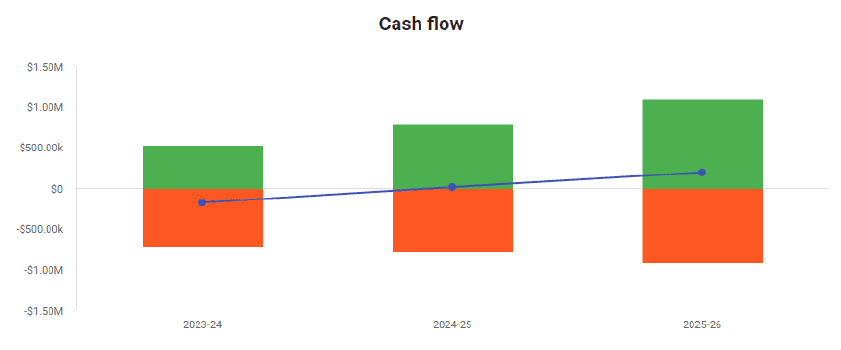
Projected Cash-Flow Statement
Projected Profit & Loss Statement
Break-Even Analysis
Improve Your Financial Planning with Upmetrics
What’s the best way to create a financial plan? If you had asked this question maybe a decade ago, I would definitely have said—EXCEL. Not today.
With the AI revolution and modern business & financial plan software, financial planning has never been this accurate before.
Want to improve your financial planning game? Upmetrics is the way to go. No manual calculations or preparing visual reports; simply enter your assumptions and watch things getting done.
What are you waiting for? Try Upmetrics for your business financial plan.